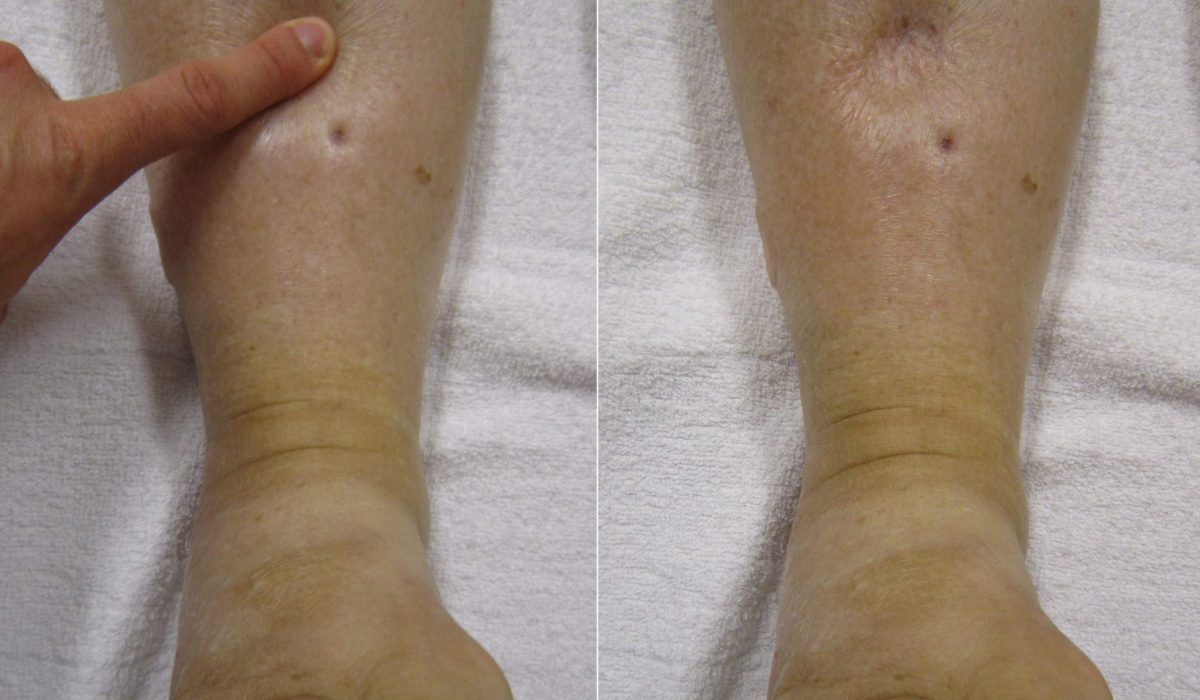
Swelling is a condition in which there is an accumulation of fluid in the tissues, leading to an abnormal increase in size. It is a common problem that affects people of all ages and can occur in various parts of the body. Swelling can be a result of injury, infection, or an underlying health condition. It is essential to understand the causes and symptoms of swelling to determine the best treatment options.
Causes of Swelling
There are many causes of swelling, including poor circulation, injury or trauma, inflammation, lymphatic system problems, medications, and underlying health conditions. Poor circulation can lead to fluid buildup in the legs and feet, while injury or trauma can cause localized swelling. Inflammation is another common cause of swelling, and it can result from an infection or injury. Lymphatic system problems can also cause swelling, as can medications such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Additionally, underlying health conditions such as heart, liver, or kidney disease, and pregnancy can also lead to swelling.
Heart, liver, and kidney disease can cause fluid to build up in the body, leading to swelling in various parts of the body. Pregnancy can also cause swelling, especially in the legs and feet. This is due to the pressure on the blood vessels and hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy.
Other causes of swelling include allergic reactions, infections, and certain medications. Allergic reactions can cause swelling, redness, and itching in the affected area. Infections, such as cellulitis or abscesses, can also lead to swelling. Certain medications, such as antidepressants, can cause swelling in the hands and feet.
It is important to identify the underlying cause of swelling to determine the best course of treatment.
Symptoms of Swelling
Swelling can cause a range of symptoms, including pain or discomfort, redness or warmth in the affected area, skin changes, limited mobility, and difficulty breathing (in severe cases). Pain or discomfort can be caused by the pressure on the tissues from the fluid buildup. Redness or warmth in the affected area can indicate inflammation or infection. Skin changes, such as tightness or discoloration, may also occur.
Limited mobility can result from the swelling's effect on the joints and tissues, making it difficult to move the affected area. In severe cases, such as with pulmonary edema, swelling can lead to difficulty breathing, chest pain, and even death.
Treatments for Swelling
Treatment for swelling depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases of swelling can often be treated at home with the R.I.C.E method, which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation. Resting the affected area, applying ice to reduce swelling, using compression bandages or stockings, and elevating the affected area can all help reduce swelling.
In more severe cases, medication may be necessary. Diuretics can be prescribed to reduce fluid buildup, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to reduce inflammation and pain.
Compression therapy, using compression stockings or bandages, can help reduce swelling in the legs and feet. Surgery may be necessary in rare cases, such as with lymphedema, to remove excess fluid and tissue.
Prevention of Swelling
Prevention of swelling involves lifestyle changes, exercise, and diet modifications. Maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing can help prevent swelling. Elevating the feet and legs, wearing compression stockings, and avoiding tight clothing can also help.
Eating a healthy diet, low in salt and processed foods, can help reduce fluid retention in the body. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding alcohol and caffeine can also help.
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help identify underlying health conditions that may contribute to swelling.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if swelling persists or recurs, or if there is a sudden onset of swelling. Emergency situations, such as difficulty breathing or chest pain, require immediate medical attention.
Persistent or recurrent swelling may indicate an underlying health condition that requires treatment. A sudden onset of swelling, especially in one part of the body, may be a sign of a blood clot or other serious condition.
Conclusion
Swelling is a common condition that can occur in various parts of the body. There are many causes of swelling, including poor circulation, injury or trauma, inflammation, lymphatic system problems, medications, and underlying health conditions. Swelling can cause a range of symptoms, including pain, redness, skin changes, limited mobility, and difficulty breathing. Treatment for swelling depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition, and prevention involves lifestyle