|
| ▲ Photo Source: Pixar Bay |
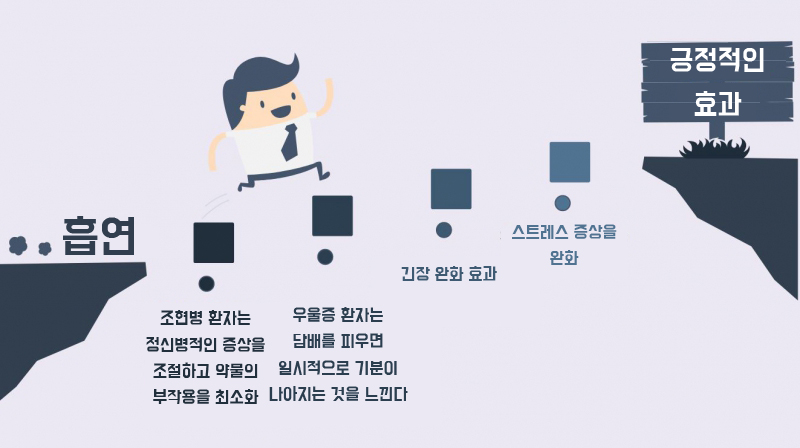
People with behavior problems or mental health problems are often smokers. Nicotine in cigarettes improves mood and concentration, reduces anger and stress, and relaxes muscles. However, these effects are soon to disappear and are likely to cause other diseases. Experts argue that smoking and mental illness are closely linked to biochemical factors. Judith Prochska, a psychologist at the Stanford Center for Preventive Research, explains that nicotine plays a role as a hallucinogen in smokers, whether or not they have a mental illness.
Some people with mental illness also smoke cigarettes to treat symptoms or reduce drug side effects. Nicotine also has the effect of boosting concentration. The chemical usually reaches the brain within 10 seconds. The brain absorbs nicotine at a rapid rate and experiences certain effects.
However, continuous consumption of nicotine can change the way the brain works. The most common side effects are withdrawal symptoms. This is why some people suffering from mental illness suffer from increased heart rate. Severe panic attacks can result. When you smoke, the symptoms stop temporarily, but the habit is strengthened and repeated. Eventually, smokers become unhappy with nicotine dependence.
 |
Side Effects of Smoking
Some people argue that smoking is also beneficial. However, smoking is easily addicted, and once it becomes habit, it is very difficult to stop. Some of the typical side effects of smoking are introduced.
1. Stress is a common condition we experience on a daily basis. When stress becomes uncontrollable, a variety of physical problems such as headaches arise, and some people become anxious and irritable. Some smoke tobacco for the purpose of alleviating stress symptoms. However, habits change behavior and the number and amount of smoking are increasing.
2. Another reason people smoke is to reduce tension. Nicotine provides immediate relief to smokers in that they reduce anxiety and stress. However, temporary relaxation causes side effects that rely on chemical and withdrawal symptoms. Finally, the habit of looking for tobacco causes anxiety and stress.
3. Smoking and depression are highly related. Nicotine stimulates the brain to release dopamine, a neurotransmitter. Dopamine is a substance that makes you feel positive, especially when you are depressed. Therefore, a person with depression feels that his / her mood is improved due to the temporary generation of dopamine when he / she smokes. However, smoking habits also make the brain lose its ability to naturally produce dopamine. The result is a long-term deprivation of neurotransmitters and, unfortunately, more frequent tobacco smoke. Thus, people suffering from depression experience more severe withdrawal symptoms than the average person, and they need a great deal of effort to overcome them.
4. Patients with cervical cancer smoke nearly three times more than the average person, and most of them are nicotine addicts. Often, patients with asthma are known to choose smoking to control psychotic symptoms and minimize adverse drug effects.
Tobacco can reduce the symptoms of people suffering from mental illness. However, smoking habit is very dangerous because it can eventually lead to physical diseases such as heart disease and lung cancer.
 |
The risk of smoking
According to the Cleveland Clinic researchers, smoking does not provide a stabilizing effect. Rather, it increases the stress of the body and has several negative effects. These include increases in cerebral blood pressure and heart rate, muscle tension, vasoconstriction, and reduced oxygen.
Tobacco can cause serious health problems such as heart disease, stroke, and increased incidence of lung cancer. Habitual smoking also affects major organs such as the bladder, kidneys, and liver. Lowering the chance of pregnancy, damaging sperm cells, and increasing the risk of miscarriage. It can cause cataracts and type 2 diabetes and weakens the immune system.
 |
Additional Information
- The World Health Organization (WHO) reported that more than 1.1 billion people smoke by 2015 and that smoking rates in the eastern Mediterranean and African regions are increasing.
In particular, young people who smoke are more likely to experience emotional and psychological problems.
- Teen smokers have three times more alcohol consumption, 8 times more likely to smoke marijuana, and 22 times more cocaine use than their peers.
- More than 7 million people die each year from tobacco-related illnesses, of which about 890,000 are victims of secondhand smoke.
- 80% of the world's 1 billion smokers live in low- and middle-income countries.
![[Health] Reasons why people with mental illness smoke health reasons why people with mental illness smoke 1](https://moontore.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/health-reasons-why-people-with-mental-illness-smoke-1-1200x700.jpg)