|
| Source: Pixar Bay |
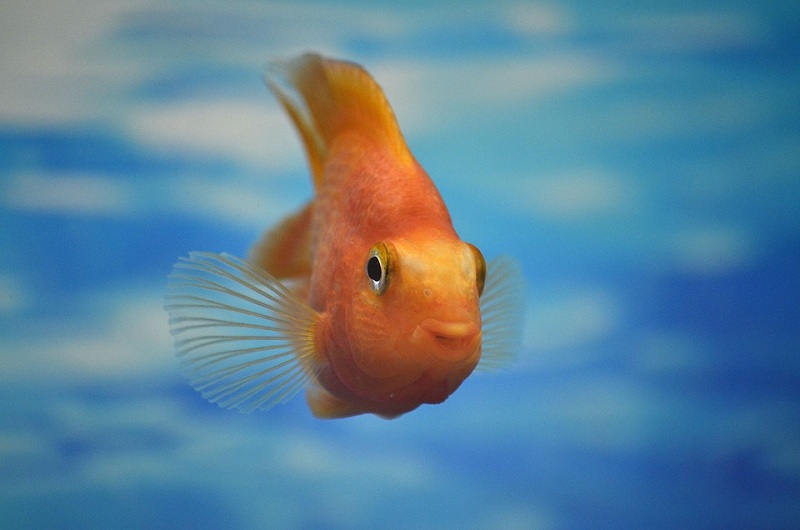
The fish that live in a fish tank also relies on sensory organs to notice what is happening around them. The senses of fish sense direction, eating, communication, invasion of enemies. Light does not move fast in water, but sound is transmitted faster and farther in the water.
Fish can see nearby objects or distant objects and can distinguish colors. However, the eyes of the fish have different visibilities depending on their location. So it depends more on hearing than vision. As mentioned earlier, the sound is much faster in the water, and the fish can hear the sound as it vibrates with the thin line that runs along the side fins of the body. This line can filter out low-frequency sounds due to background noise and environmental changes.
In addition, fish also taste and smell. This is called chemical acceptance or chemical sensitization. Fish can use the receptors of the mouth and nose openings to find food and communicate with other fish. Fish can detect changes in the environment through electricity, which is called electricity reception. Fish can use low-level electric fields and send electrical signals from nearby organs and signals to receptors on the head and the side lines. This sense can detect food or obstacles in dark water.
![[Pet] Sensory organ of pet fish pet sensory organ of pet fish](https://moontore.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/pet-sensory-organ-of-pet-fish-1200x700.jpg)