A dog who helps a lot of people live. Although the benefits and benefits of puppies are already well known, they have recently been identified as a factor in prolonging human life. Let's explore the deep link between puppy and human being.
Longevity benefits?
Studies conducted by Uppsala University in Sweden for 3.4 million people over the last 12 years show that dogs raise the risk of developing cardiovascular disease. It attracts more attention, especially in people who live only with other roommates or puppies, not with their families.
Studies have shown that people living alone have a 33 percent lower risk of death and a 11 percent lower risk of heart attack.
Mwenya Mubanga, a researcher at the Uppsala University Life Sciences Institute, said that it is interesting to note that puppies have a better impact on people living alone than those living with other people. This proves that the existence of a puppy is very important to the family living alone.
However, this study did not reveal how dog breeding is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. If you live with dogs, it seems to help protect your healthier habits.
Professor Tove Fall of the Department of Veterinary Medicine also said that dogs play a role in providing the necessary social support to make people more active and active. For example, if you take a walk with your dog, it will help your carers to exercise and exercise unconsciously as well as forming a bond.
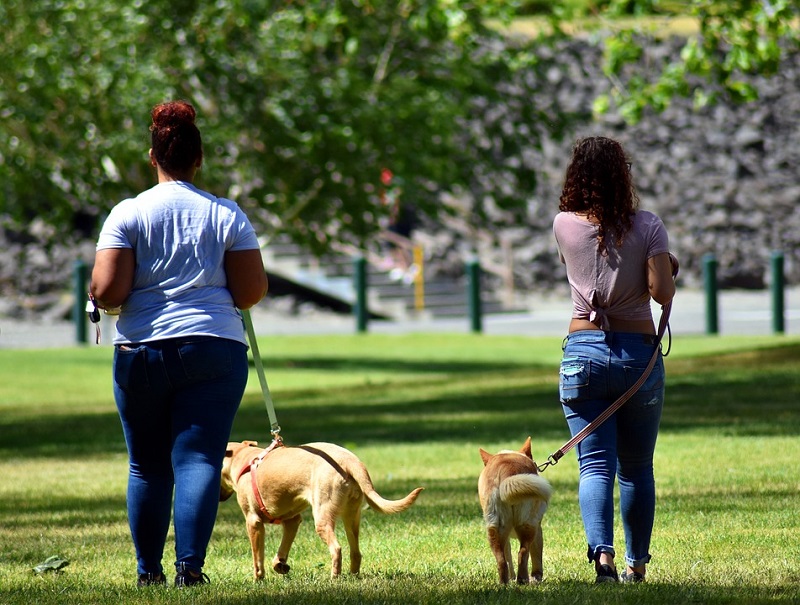 |
| (Source: Pixar Bay) |
Dog-to-human link
Dogs are not merely useful for human life. In fact, it has been proven that there are many similarities found in the relationship between humans and dogs.
First, it was found that there is a similar gene between a dog born to developmental disorder and a dog. A study published in the Science Advance magazine found similar parts of the human chromosome with Williams-Beuren Syndrome (WBS), one of the human disorders. This syndrome is a disorder that affects the intellectual ability of a human being. A person born with this disorder is very sociable and emotional, loves to meet his / her eyes for a long time, and does not care much. However, it has a mild degree of intellectual ability and anxiety.
Domestication is another link. Monique Udell, a zoologist at the Oregon University, explained that dogs, unlike wolves, developed an advanced form of social awareness that seeks social contact with humans. This means that you have the ability to communicate with humans.
The team observed how 18 puppies and 10 gray wolves reacted to humans in the course of problem solving. As a result, when dogs and wolves were offered boxes of equally preyable food, the dogs behaved to look for them in nearby neighborhoods with more people than wolves. The wolf, on the other hand, was strong in his own efforts to solve it.
It was also found that the genetic prop- erties of dogs were related to their supersocial propensity. It seems that GIF21 and GTF2IRD1 genes have become important factors in the animalization of dogs. This gene was not found in the wolf.
 |
| (Source: Manhattan's 514th Aerial Flying Squadron) |
Other health benefits
There is another discovery that proves that dogs are beneficial to humans. The dog affects the microbes in the body of the protector. For example, children living with dogs at home are less at risk of developing allergies and asthma. It is an explanation that living in the same environment with dogs can strengthen human immune system. Stress reduction and blood pressure recovery were also faster.
Other studies have shown that carers who breed varieties raised for hunting, such as terriers and rat-rivers, have the lowest risk of heart disease. This is thought to be because the physical activity such as exercise is essential because of the nature of raising big dogs, so they exercise more often.
![[Issue] Dog grows longer? A variety of dogs and human ‘linkage’ issue dog grows longer a variety of dogs and human linkage](https://moontore.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/issue-dog-grows-longer-a-variety-of-dogs-and-human-linkage-1200x700.jpg)